Queanbeyan
Please note: Text or data highlighted in this colour represent an update to this indicator for the period 2008/09. All rainfall figures have been updated on this page.
Rainfall Analysis
The main rainfall observing site used in this analysis was Queanbeyan Bowling Club (Bureau of Meteorology Station No. 070072), which has records commencing in 1871.
Note that in the following analyses rainfall totals for individual months or years (where the year is defined as the 12 months from July to June) are compared to the long-term average (or climatology) from 1961-1990. A 30-year period is used to calculate climatological averages to conform with World Meteorological Organisation practice; this takes into account year-to-year variations and less frequent events such as El Niño or La Niña. This particular 30-year period is used internationally as a standard climatological average period.
As shown in the table below, Queanbeyan was drier than average for four of the five years in the period 2004/05-2008/09. The driest year was 2007/08, when rainfall was 21.1% below the long-term average at 476.6 mm for the year. The wettest year was 2005/6 where rainfall was 9.8% above average with 663.0 mm.
| Rainfall Statistics | Queanbeyan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2004/5 |
2005/6 |
2006/7 |
2007/8 |
2008/9 |
|
| Annual Total* (mm) | 573.8 |
663.0 |
497.6 |
476.6 |
533.4 |
| Anomaly (mm) | -30.3 |
58.9 |
-106.5 |
-127.5 |
-70.7 |
| Anomaly (%) | -5.0 |
9.8 |
-17.6 |
-21.1 |
-11.7 |
| Mean (1961-1990) (mm) | 604.1 |
||||
*Note: annual totals were calculated for the 12 months July-June.
Monthly Rainfall, 2004-2009
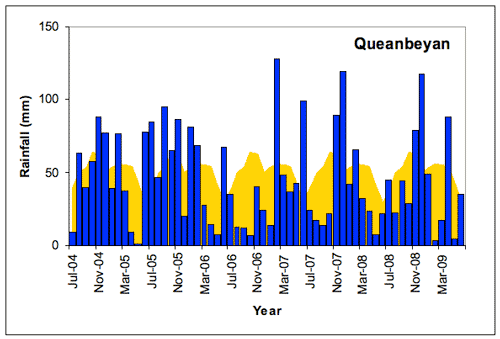
A comparison of monthly rainfall totals with the long-term monthly average rainfall at Queanbeyan (Figure 1) shows that the for the first half of the record was generally above average apart from short periods of dry months while the second half of the period was generally dry with isolated wet months. The prolonged dry period through 2006/7 was related to the El Niño event that was experienced during that time while the wet period November 2007 to February 2008 was related to the development of a La Niña event as was the rainfall in November-December 2008.
 |
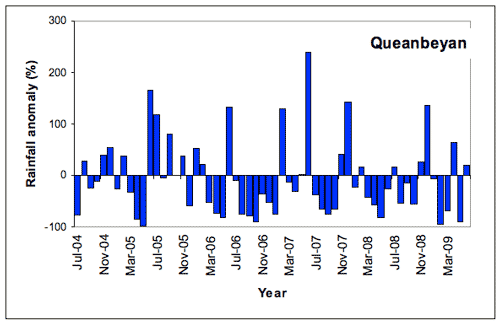
Of the 60 months in this period, 37 months (62% of the record) experienced below-average rainfall at Queanbeyan (Figure 2). The most prolonged dry spell began in March 2006 and extended to January 2007, with above-average rainfall in June 2006. Shorter dry period occurred in autumn 2005, June to October 2007 and March to June October 2008. February to June 2009 was again very dry apart from May 2009. The driest individual month was May 2005 with 1 mm (the long-term average for May is 41.6 mm). Generally average rainfall occurred between August 2004 and February 2005. Generally above average rainfall was recorded during May 2005 to February 2006 apart from December 2005 and also November 2007 to February 2008. Well above rainfall was also recorded in February 2007 and June 2007. The wettest individual month was February 2007 with 128.2 mm (long term average for February is 55.9 mm) while December 2007 recorded 119.6 mm. The February total was the seventh highest total for February on record back to 1871.
 |
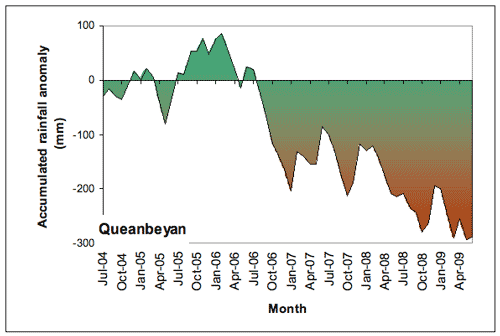
The accumulated rainfall for the period (Figure 3) indicates that the accumulation became positive in 2005 and early 2006 before a rapid increase in a deficit during the latter half of 2006. This deficit decreased during 2007 before increasing again during 2008 and see-sawing through 2009 according to the periodic wet and dry periods that were experienced during this time but generally the deficit remained flat. The total deficit for this period was 289.2 mm (48% of Jul-Jun average).
 |
The climatological context for rainfall at Queanbeyan
The long-term perspective
As is typical of the region, Queanbeyan has experienced large fluctuations in annual (July-June) rainfall, including several extended periods of above- or below-average rainfall since records began in 1871. In general, annual rainfall was lower and less variable early in the 20th century, followed by a period of greater variability (Figure 4). The recent dry period is reflected in other parts of the long term record such as the 1870’s, the late 19th and early part of the 20th Century and the period from the late 1920’s through to the end of World War II and the late 1970’s to early 1980’s. To this point in time this recent dry period can only be considered as part of the long term variability in rainfall experienced in the region.
Rainfall in the late 19th and early 20th century was generally below average (to about 1920). There were also dry periods in the early 1930s and the late 1940s. Since then annual rainfall totals have been more variable.
- Several wetter-than-normal years around 1950 and 1960 produced a generally wetter period then; the same is true of the mid 1970s.
- A sustained drier period around 1980 was followed by slightly above-average rainfall until the early 1990s. Since 1997 conditions have tended to be drier than average.
The wettest year (July-June) on record was 1947/8 (1044 mm); the driest year was 1885/6 (320 mm).
![Figure 4. Annual (July-June) rainfall at Queanbeyan from 1871/2 to 2008/9 depicted as deviations from the long-term mean. A 5-year running mean is superimposed to highlight wetter and drier periods. [Deviations were calculated as the difference between the rainfall for each year and the mean for the period 1961-1990 (scale in mm).]](../images/queanbeyan/rain04.gif) |
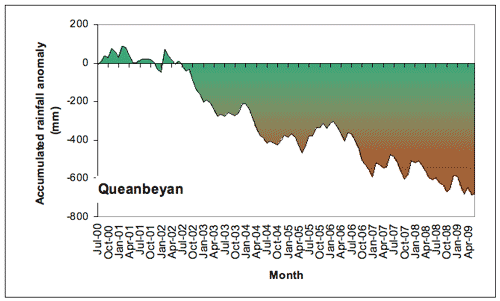
An accumulating rainfall deficit has prevailed in Queanbeyan since 2002 (Figure 5), easing only slightly in 2005. This reflects the impacts of the two El Niño years of 2002-3 and 2006-7 without a compensating wet period. During the whole period there were 70 months (65%) of rainfall deficit and the total accumulated deficit was 678.7 mm (112% of the average Jul-Jun rainfall).
 |
About the data
